Overview
Metal casting is a vital manufacturing process that involves pouring liquid alloy into a mold, allowing for the creation of a wide range of products, from beautiful jewelry to essential automotive components.
We understand that the versatility of different casting techniques, such as sand casting and investment casting, plays a crucial role in meeting industry demands. This is especially true in sectors like automotive and aerospace, where precision and innovation are paramount.
By exploring these techniques, we can appreciate how they contribute to the quality and functionality of the products we rely on every day.
Introduction
Metal casting is not just a process; it’s a vital aspect of our manufacturing world, influencing everything from delicate jewelry to sturdy automotive parts. As we witness a growing demand for high-quality, precision-engineered components—projected to boost the alloy production market to nearly $268 billion by 2037—it’s crucial to appreciate the intricacies of metal casting. Are you curious about how to navigate the complexities of various casting techniques and their applications? This exploration invites you to delve into the rich history, diverse methods, and essential steps of metal casting, shedding light on its indispensable role in modern production and innovation.
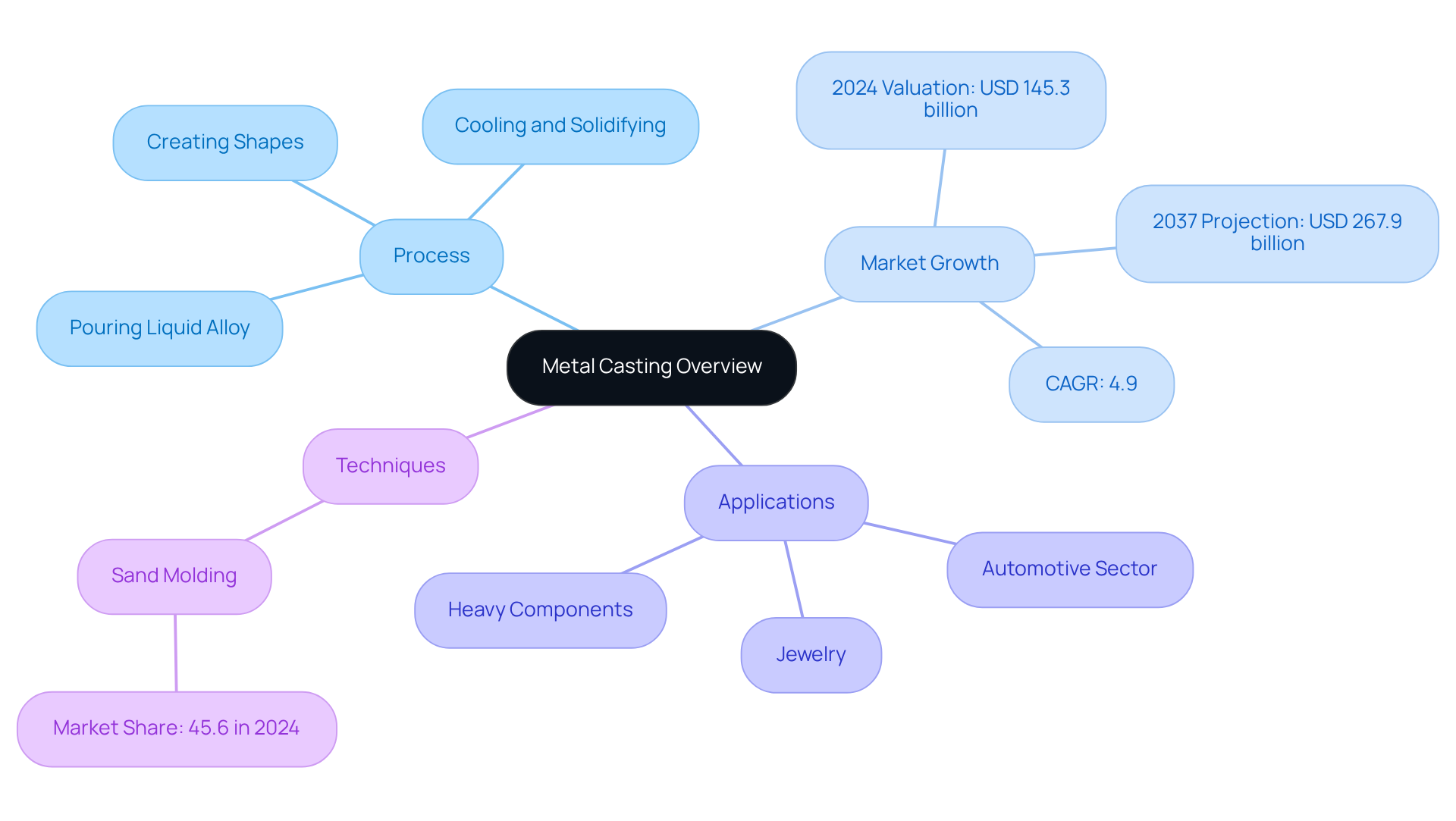
Defining Metal Casting: An Overview
Metal cast is a crucial manufacturing process that involves pouring liquid alloy into a mold, capturing the negative impression of the desired shape. As the liquid cools and solidifies, it takes on the mold’s form, enabling the creation of three-dimensional objects. This technique is vital for producing a wide range of products, from delicate jewelry to substantial products made through metal cast processes. The versatility of alloy molding is especially impressive, allowing for the crafting of intricate shapes that are often difficult to achieve with other methods.
Did you know that the global alloy production market was valued at USD 145.3 billion in 2024? It’s projected to reach USD 267.9 billion by 2037, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.9% from 2025 to 2037. This growth is largely fueled by rising demand across various industries, especially in , which represented about 51.5% of the market share in 2024. Industry experts emphasize the importance of alloy shaping in manufacturing, especially in the metal cast process, which is crucial for producing high-quality parts that meet stringent design and safety standards.
Consider the real-world applications of metal cast techniques. The automotive sector, for instance, relies heavily on this process for manufacturing engine components, transmission parts, and body assemblies, which account for the largest application segment with a market share of 28.5%. Additionally, advancements in molding technologies have enabled manufacturers to create lightweight and fuel-efficient vehicle parts, aligning with the growing trend towards hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), which dominate the electric vehicle market with a remarkable share of 90.1%.
Furthermore, sand molding leads the market with approximately 45.6% market share in 2024, showcasing its flexibility and cost-effectiveness in producing large components. Overall, alloy shaping not only enhances manufacturing capabilities but also promotes innovation and efficiency across various sectors, establishing it as a cornerstone of modern production techniques.
Historical Development of Metal Casting Techniques
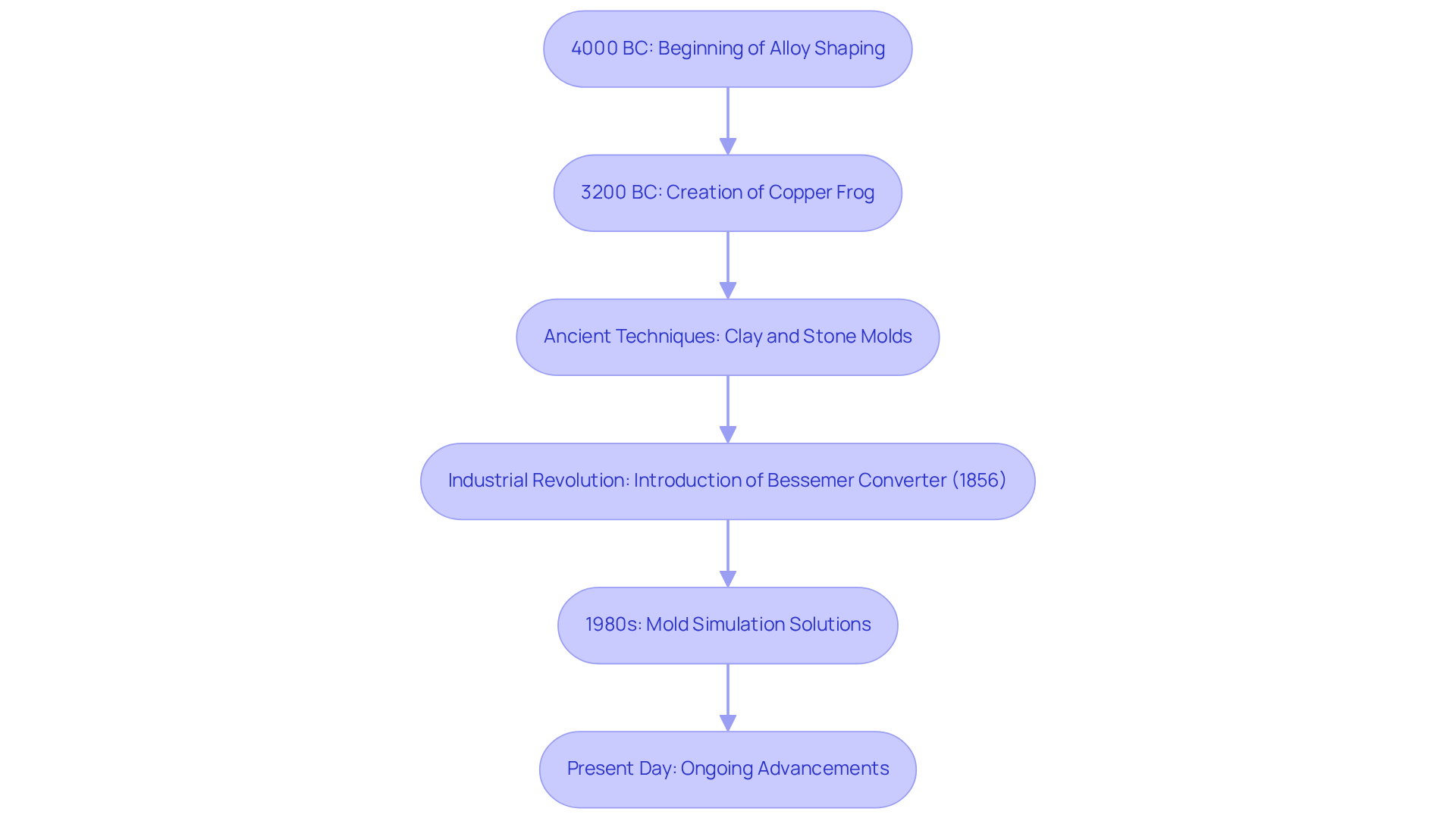
The history of alloy shaping is a fascinating journey that dates back to around 4000 BC. We can trace the earliest evidence to ancient Mesopotamia and China, where significant artifacts, such as the remarkable copper frog made around 3200 BC, were created. Early forming methods relied on simple molds crafted from clay or stone, primarily used for precious materials like gold and copper. As civilizations evolved, so too did the techniques for shaping these metals, leading to the introduction of more sophisticated methods like sand molding and lost-wax molding.
Furthermore, the Industrial Revolution marked a pivotal moment in metal production. It brought forth innovative materials and technologies, including the Bessemer Converter, discovered by Sir Henry Bessemer in 1856. This invention greatly enhanced the precision and efficiency of the manufacturing process, addressing the growing demands of the time. In addition, the advent of mold simulation solutions in the 1980s revolutionized the industry, allowing for more accurate predictions of material behavior. This means that the era not only transformed the manufacturing landscape but also laid the groundwork for contemporary molding techniques.
Today, the metal cast process is essential across various industries, continually evolving through advancements that improve both quality and production capabilities. Initiatives like the Department of Energy’s Metal Molding Competitiveness Research Act, enacted in 1990, highlight the ongoing significance of this field. We understand that the world of can seem daunting, but it is a testament to human ingenuity and progress, reflecting our commitment to innovation and excellence.
Types of Metal Casting Processes and Their Applications
Metal cast is a multifaceted process designed to meet a variety of applications and manufacturing needs. Are you curious about how these methods can impact your industry? Let’s explore some of the most common techniques:
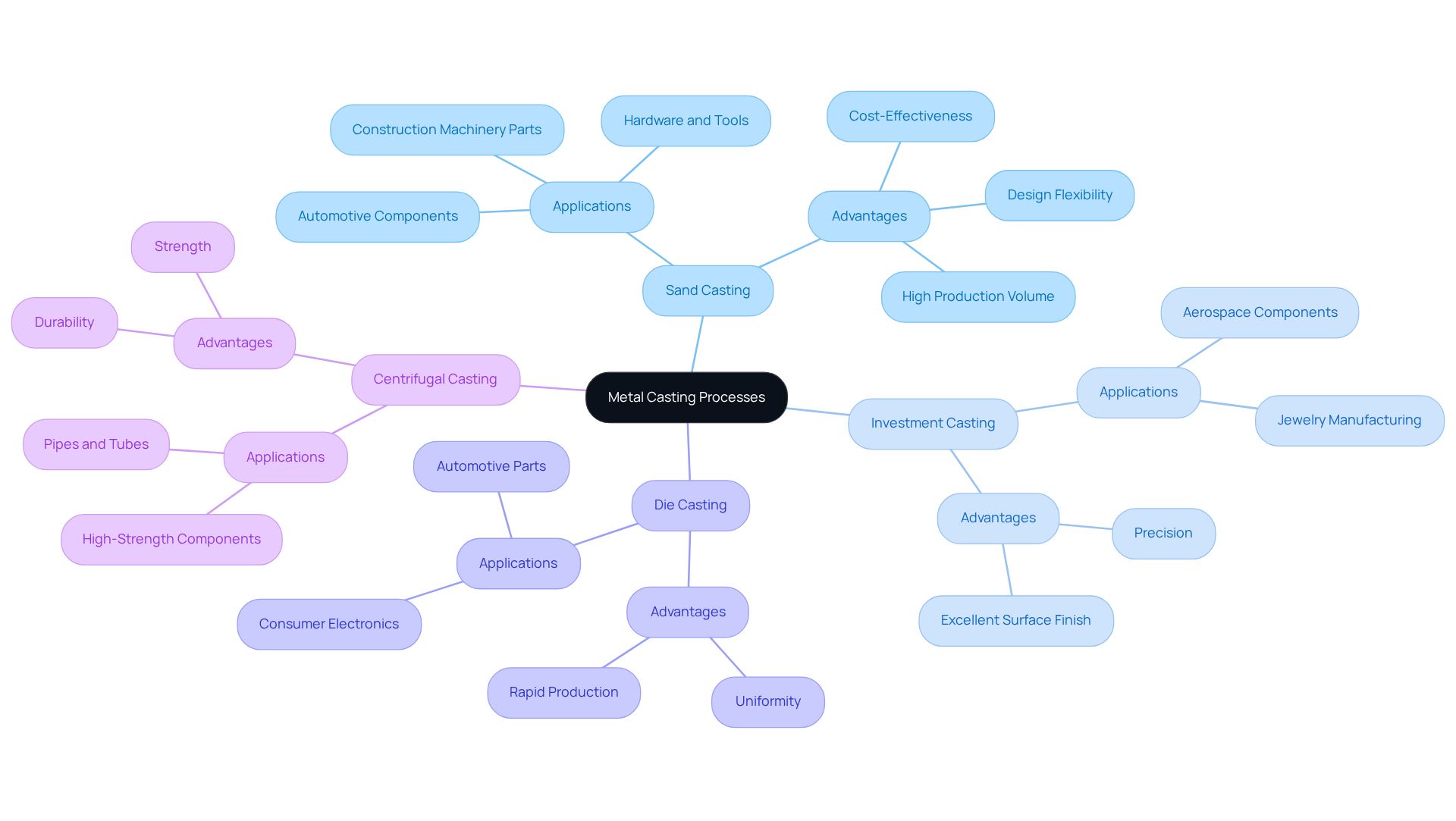
- Sand Casting: This widely used process creates molds from sand, making it perfect for producing large and complex parts. It’s especially prevalent in the automotive sector for components like engine blocks and transmission housings, where flexibility and cost-effectiveness are essential. Did you know that sand molding accounts for over 70% of global production? This highlights its significant role in the market. The advantages of design flexibility and reduced waste make it a go-to choice for many manufacturers.
- Investment Casting: Also known as lost-wax casting, this method is celebrated for its precision. It’s particularly suitable for intricate components in industries such as aerospace and jewelry. This technique allows for the creation of complex geometries with excellent surface finishes, meeting the stringent demands of high-performance applications. Your need for precision is met here.
- Die Casting: This method involves injecting liquid alloy into a mold under high pressure, making it ideal for the mass production of small to medium-sized components. It finds common use in consumer electronics and automotive applications, where uniformity and rapid production are vital. We understand that efficiency matters to you.
- Centrifugal Casting: By utilizing centrifugal force, this method distributes molten material into a mold, effectively producing cylindrical parts like pipes and tubes. It’s particularly advantageous for creating components that require high strength and durability. Your projects deserve robust solutions.
Each molding technique offers unique benefits, providing flexible production options across various sectors, including automotive and aerospace. As the global metal cast market is projected to reach USD 225.7 billion by 2032, the significance of these processes in modern manufacturing is undeniable. Furthermore, UK foundries produce precision-engineered components valued at around £2.2 billion annually, underscoring the economic impact of this industry. We recognize the importance of innovation, and the integration of is emerging as a testament to the relevance of these practices in today’s manufacturing landscape.
Key Steps in the Metal Casting Process: From Patternmaking to Finishing
The metal casting process encompasses several essential steps that are vital for producing high-quality components, and we understand how important each of these stages is for achieving the best results:
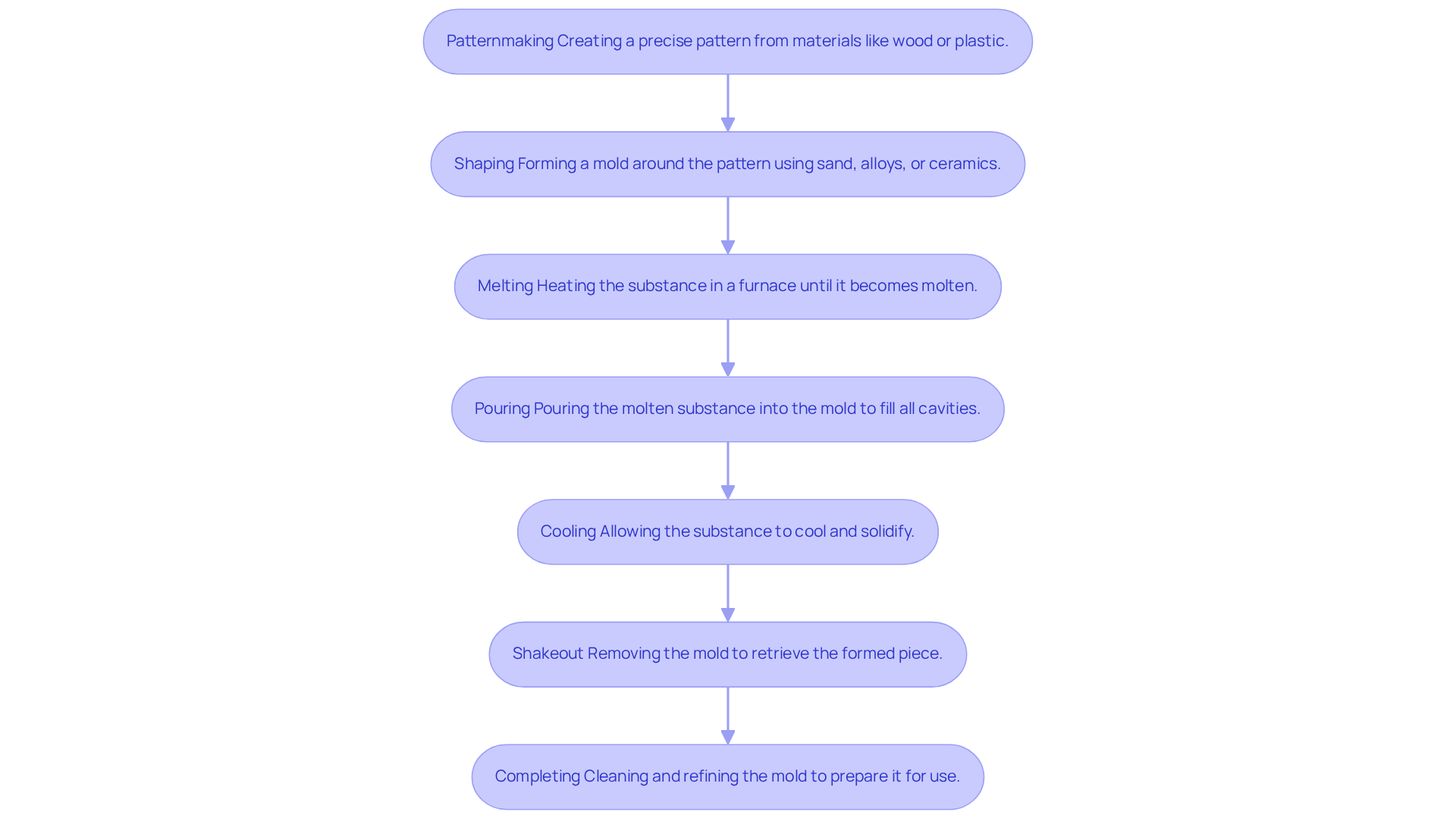
- Patternmaking: This initial phase involves creating a precise pattern that mirrors the desired object. Patterns are usually crafted from materials like wood, plastic, or others, and their accuracy is crucial for the success of the mold. Traditionally, on a single piece, emphasizing the time and care that goes into this critical step.
- Shaping: In this step, a form is created around the pattern. The form can be made from various substances, such as sand, alloys, or ceramics, based on specific shaping needs.
- Melting: The substance is heated in a furnace until it reaches a molten state. This process requires meticulous temperature control to ensure optimal fluidity, reflecting our commitment to precision.
- Pouring: The molten substance is then poured into the mold, ensuring that it fills all cavities to create a complete form. Precision during this step is critical to avoid defects, and we know how disappointing it can be to face imperfections.
- Cooling: After pouring, the substance must cool and solidify. The cooling duration can vary greatly depending on the type of alloy and the thickness of the mold, influencing the final product’s characteristics.
- Shakeout: Once the alloy has cooled, the mold substance is carefully removed to retrieve the formation. This step requires gentle handling to prevent damage to the newly formed piece, as we want to ensure its integrity.
- Completing: The last stage includes cleaning and refining the mold to remove flaws and prepare it for its intended purpose. This may involve trimming, polishing, or applying protective coatings, ensuring that every detail is attended to.
Each of these steps plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards. Industry experts highlight that careful attention to detail during patternmaking and molding can significantly enhance the overall success of fabrication projects. Furthermore, advancements such as 3D printing allow foundries to produce intricate and customized patterns directly from digital designs, reducing lead times. As noted by Badger Alloys, “Pattern making is a critical component in the metal cast manufacturing process, serving as the blueprint for casting metal parts.” We understand that investing in quality processes leads to better outcomes, and your satisfaction is our priority.
Conclusion
Metal casting stands as a foundational process in modern manufacturing, enabling the transformation of liquid alloys into precisely shaped components that meet diverse industry demands. This intricate technique not only facilitates the production of a wide range of products but also underscores the significance of innovation and efficiency in manufacturing practices.
Throughout the article, we explored key insights into metal casting, including its historical evolution and various processes such as:
- Sand casting
- Investment casting
- Die casting
Additionally, we discussed the critical steps involved in the casting process. The impressive market growth projected for the metal casting industry highlights its vital role in sectors like automotive and aerospace, where precision and reliability are paramount.
Reflecting on the importance of metal casting, it becomes clear that this process is not just a manufacturing method but a catalyst for technological advancement and economic growth. As industries continue to evolve, embracing innovations such as 3D-printed molds, the relevance of metal casting will only increase. Are you ready to engage with these advancements? Doing so not only enhances production capabilities but also fosters a commitment to excellence in design and safety standards. Embracing the potential of metal casting can pave the way for future innovations, ensuring that the industry remains at the forefront of manufacturing excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is metal casting?
Metal casting is a manufacturing process that involves pouring liquid alloy into a mold to create three-dimensional objects. As the liquid cools and solidifies, it takes on the shape of the mold.
What are the applications of metal casting?
Metal casting is used to produce a wide range of products, from delicate jewelry to substantial components in various industries, particularly in automotive and transportation.
How large is the global alloy production market?
The global alloy production market was valued at USD 145.3 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 267.9 billion by 2037, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.9% from 2025 to 2037.
Which industry represents the largest market share in alloy production?
The automotive and transportation industries represented about 51.5% of the alloy production market share in 2024.
What role does metal casting play in the automotive sector?
The automotive sector relies on metal casting for manufacturing engine components, transmission parts, and body assemblies, which account for the largest application segment with a market share of 28.5%.
What is the significance of advancements in molding technologies?
Advancements in molding technologies have allowed manufacturers to create lightweight and fuel-efficient vehicle parts, supporting the trend towards hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), which hold a significant share of the electric vehicle market.
What type of molding leads the market in alloy production?
Sand molding leads the market with approximately 45.6% market share in 2024, due to its flexibility and cost-effectiveness in producing large components.
How does alloy shaping impact manufacturing?
Alloy shaping enhances manufacturing capabilities, promotes innovation, and increases efficiency across various sectors, making it a cornerstone of modern production techniques.